Introduction to AI in Society
Week 1: Foundations and Overview
Agenda
- AI Impact Case Studies
- Why AI Literacy Matters
- Understanding Modern AI
- Core Competencies & Skills
- Course Structure & Assessment
- Tools & Getting Started
AI In Society
Alphafold
Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2024:
“Chemists have long dreamed of fully understanding and mastering the chemical tools of life – proteins. This dream is now within reach. Demis Hassabis and John Jumper have successfully utilised artificial intelligence to predict the structure of almost all known proteins. David Baker has learned how to master life’s building blocks and create entirely new proteins. The potential of their discoveries is enormous.”

303 newly discovered relief-type figurative geoglyphs from the AI-assisted survey (PNAS)
Commonwealth Bank of Australia (CBA) has reported impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on its customer service, reducing scam losses and expedite loan processes.
The bank, which serves over ten million customers, claims to have seen a 50% reduction in scam losses and a 30% decrease in customer-reported frauds*, as a result of AI-driven safety features such as NameCheck, CallerCheck, and CustomerCheck.

The team is training an algorithm to piece together fragments that have yet to be situated in their proper context. Already, the algorithm has newly identified hundreds of manuscripts and many textual connections. In November 2022, for example, the software recognized a fragment that belongs to the most recent tablet of the Gilgamesh epic, which dates from the year 130 BC—making it thousands of years younger than the earliest known version of the Epic.
Why AI Literacy Matters
Current Adoption & Impact
39% of U.S. population (18-64) use generative AI
24% of workers use it weekly
Nearly 1 in 9 workers use it daily (Bick et al., 2024)
OpenAI: 300 million weekly active users (Dec 2024)
Why Now?
- Rapid workplace adoption showing significant productivity gains (Dell’Acqua et al., 2023, Brynjolfsson et al., 2023), though a ‘jagged technological frontier’ with uneven benefits
- New regulatory requirements emerging globally (EU AI Act, 2024)
- Rising concerns about AI-generated misinformation (Williamson & Prybutok, 2024)
- Growing digital divides in AI capabilities
- Increasing workplace expectations for AI competency
Productivity Implications
- 34% improvement for novice and unskilled workers (Brynjolfsson et al., 2023)
- 18% increase in writing quality with 40% time savings, and increased satisfaction with work (Noy & Zhang, 2023)
Great AI Literacy Divide
- Greater susceptibility to AI-generated misinformation, AI Slop
- Challenges distinguishing between accurate information and AI hallucinations
- Workplace disparities in access to AI’s productivity benefits (and more vulnerability in a capitalist economy)
Risk Imbalance
- The benefits of AI are uneven, as are the risks
- Women and people of color express more concerns about AI adoption (Yu et al., 2021)
- Underprivileged users face heightened exposure to harmful content (Madden et al., 2017)
Critical Engagement Needed
- These systems increasingly mediate crucial decisions in our lives
- We don’t want and shouldn’t cede that power to the few
- Significant need for informed, nuanced criticism
- Also need skills to evaluate AI appropriately and push back when needed
We’re getting into a trap here. People are more productive and like working with AI tools. At the same time, there are critical risks of power, inequity, and pontential harm. Those incremental short-term benefits will keep nudging us toward an AI future, regardless of the risks, creating new inequities through a literacy divide in their wake.
To look ahead and acknowledge the risks, we can’t afford to disengage. We need to be active participants in how AI systems can be used, and we need support AI literacy for all
Disambiguation system, use, and effect
Another critical need is having the language to discuss AI systems, their use, and their effects.
Are problems with the system or how it’s used? Are fears about AI really just fears about capitalism, as Ted Chiang suggests, where anything that makes us more productive isn’t applied to making our lives easier, but toward producing more for the owners of capital with less labour?
This affects how constructive we can be in considering usage, it affects how we think about legislation, and how we think about it’s place in society.
About this class
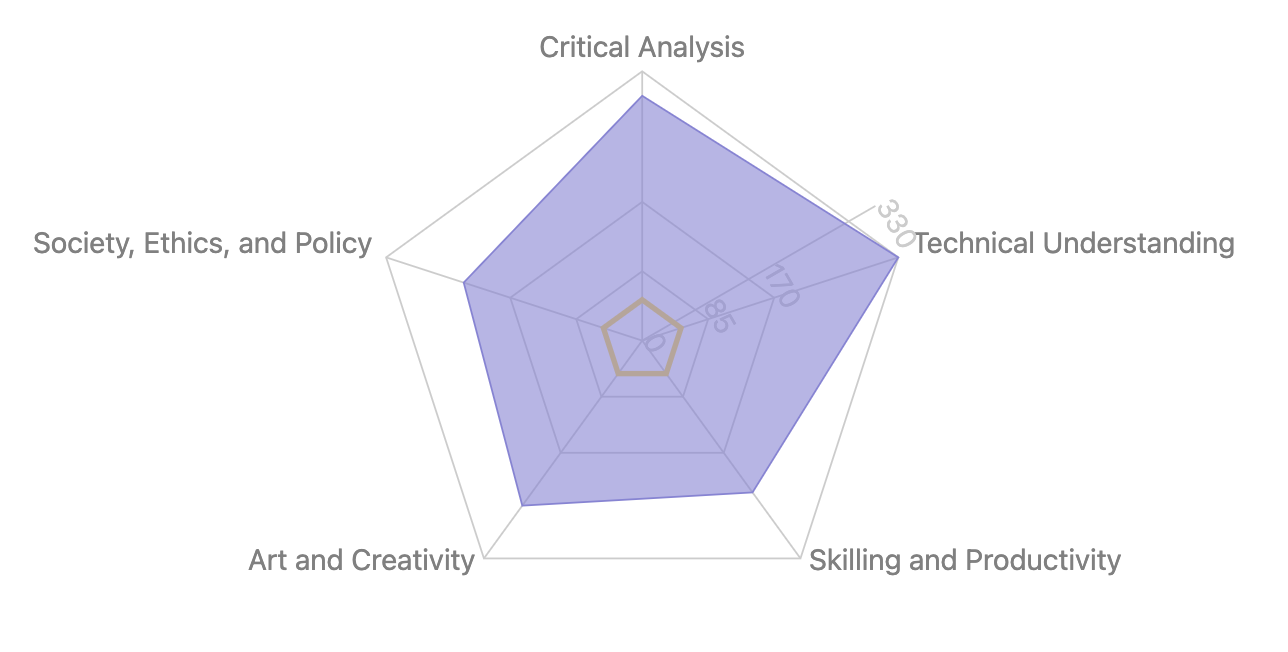
Core Competencies
- Critical Analysis, Fluency, and Evaluation
- Society, Ethics, and Policy
- Technical Understanding
- Skilling and Productivity
- Art and Creativity
Introductions
In small groups, introduce yourself, where you’re from and what program you’re in. Then, take a few minutes to discuss:
- What experiences do you already have with AI tools?
- What concerns do you have about AI use?
- How do you think AI might affect your future career?
When we reconvene we’ll do a quick set of full-class introductions.
Course Structure
Five Modules
- Introduction and Technical Foundations (Weeks 1-2)
- Working with Generative AI Systems (Weeks 3-5)
- Information Access and Analysis (Weeks 5-6)
- Ethics, Bias, and Governance (Weeks 7-8)
- Advanced and Emerging Topics (Weeks 9-10)
Assessment Overview
- Lab Portfolio (700pts)
- Progress Report (75pts)
- Final Portfolio (625pts)
- Class Participation (150pts)
- Lab Participation (150pts)
I want a system to do my laundry

Creativity in the Class: Going the Right Direction
A tool that can help you learn and execute better can free you to be more creative.
Goals of this class
- Collaborate with AI, don’t step aside for it
- Free up space for our ideas to shine, not to cede our ideation and creativity
- Open-ended labs by design
- Focus on creativity and appropriateness
- Emphasis on thoughtful integration
- Building on existing skills
Tools We’ll Use
Primary Platforms
- Claude - https://claude.ai
- ChatGPT - https://chat.openai.com
- Google AI Studio - https://aistudio.google.com
- Google Gemini - https://gemini.google.com
Optional Local Tools
- Llama + Ollama
- Open Web UI
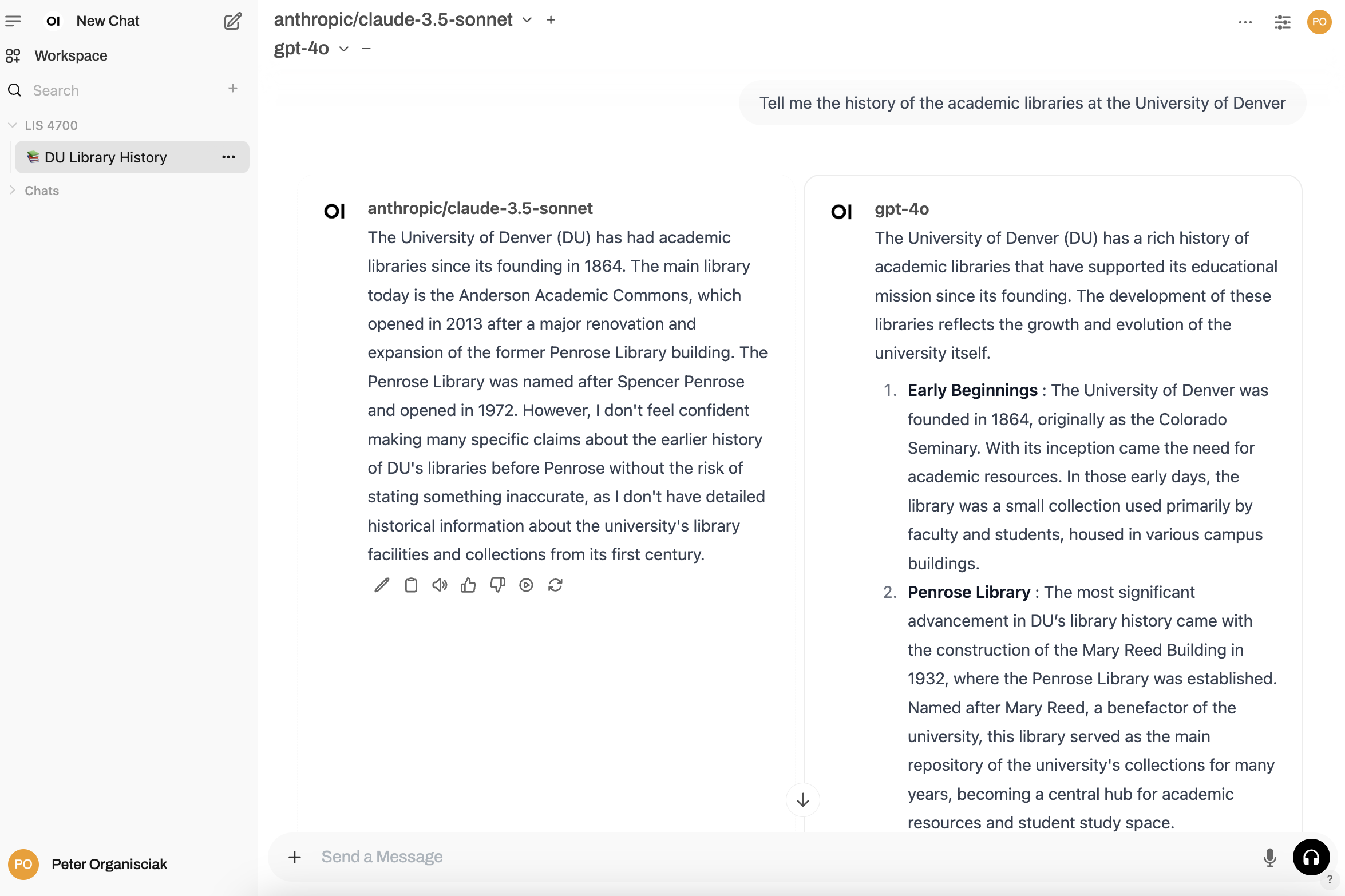
Getting Started
- Create accounts on a hosted platform (e.g. OpenAI, Gemini, Claude) if you don’t already have one
- Help out others if it’s their first time
- Begin exploring AI tools
- Complete Lab: Tool Evaluation Journal